Identification of sequencing chemistry breakdown
- The traces show a progressive decline in average quality the longer the tray sat on the instrument (i.e. sample run straight after the sequencer is loaded shows better overall quality than samples injected after sitting in the machine stack for 12+ hours).
- Re-injection of the sample after sitting in the instrument show much poorer quality the original injection traces.
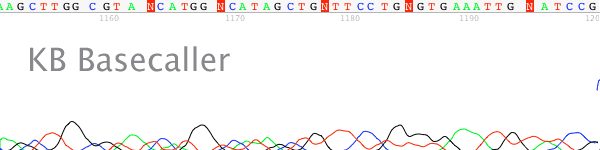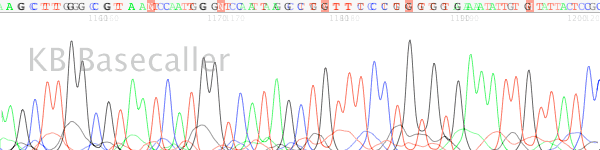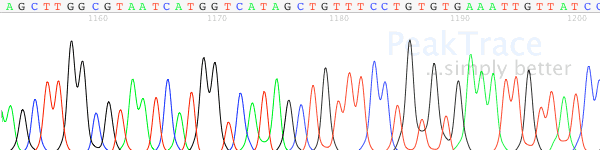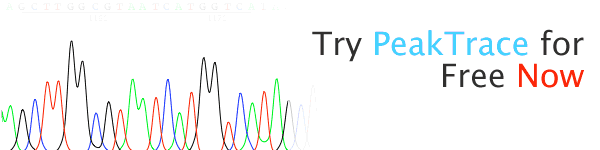
- Signal strength drops off rapidly in the raw channel – a “ski-slope” trace (Figure 1).
- By automatically track the average quality across the tray by using software like QualTrace III. This will allow you to identify chemistry breakdown problems in production before they become serious.
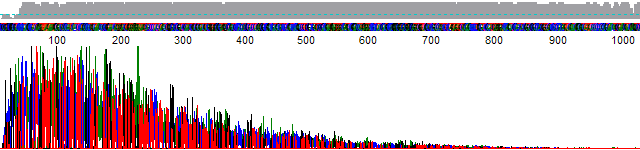
Figure 1. True profile of trace suffering from chemistry breakdown.
Causes of sequencing chemistry breakdown
- Storage of the cleaned up DNA sequencing sample in solutions of low pH for extended periods. This occurs particularly when samples are re-suspended in water. The pH of pure water drops to below pH 5.5 when exposed to air due to the absorbance of CO2. This is not generally a problem if the samples are loaded straightaway, however, if they sit on the machine overnight before the samples are loaded then they are quite likely to be damaged.
- Nuclease contamination. This is also more likely to be a problem with samples resuspended in water rather than EDTA.
Solving sequencing chemistry breakdown
- Re-suspend the DNA sequencing samples in 50 µM EDTA, pH 7.4. It is important that the 50 µM EDTA solution’s pH is adjusted AFTER dilution from stock EDTA solution.
- Only re-suspend sample just before injection on the instrument. Don’t stack up a dozen trays and let sit for hours at room temperature.
- Only load one or two trays onto the machine at a time. This will help avoid having the samples sitting around for a long time at room temperature.
Overall, the simplest way to solve this problem is to use 50 µM EDTA pH 7.4 to re-suspend the samples instead of water. This approach also has the advantaged of inhibiting nuclease activity as well as preventing overloading of the sequencer capillaries.
Return to the main DNA sequencing troubleshooting page.