Identification of template insertion and deletions problems
- The trace appears excellent before the indel region and mixed after the indel region (Figure 1).
- The trace often has a trailing ‘shifted’ peaks where a small peak is found under each primary peak (Figure 2).
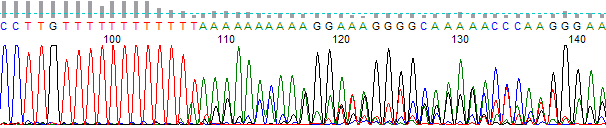
Figure 1. Example of indel trace. Note the mixed sequencing after the twelve base T run.
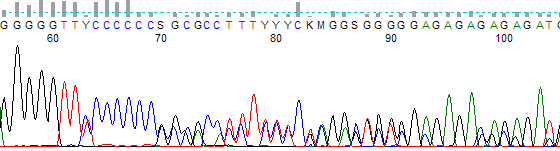
Figure 2. Example of ‘shifted’ peaks due to a template indel. Note the small G peak preceding the large single G peak present after the six C run.
Causes of template insertion and deletion problems
- Direct sequencing of PCR products derived from polymorphic templates. The most common cause of this is when directly sequencing PCR products amplified from diploid templates with heterozygous regions.
- Random mutations that have occurred during the cloning process or during plasmid mini prep process. This is much more likely to occur if the cloned template is toxic or unstable in the E. coli host.
Solving template insertion and deletion problems
- Clone the PCR products before sequencing if the template is heterozygous.
- If the template is unstable in common E. coli vectors the pUC try cloning into a low copy vector or using a different E. coli strain.
- Sequence the template from the other direction using a reverse primer. This option is more viable for small inserts, but it can be accomplished by primer walking.
For more information on detecting DNA sequencing trace problems please visit the QualTrace DNA sequencing analysis software page.
Return to the main DNA sequencing troubleshooting page.
